扫码下载APP
及时接收考试资讯及
备考信息
c) Contingency Theories(权变理论)
Contingency theories are a class of behavioural theory that argues there is no single, best way of leading. The leader's ability to lead is contingent on various situational factors, including the leader's preferred style, the capabilities and behaviours of followers and other situational factors.
An effective leadership style in some situations may not be successful in others. An effect of this is that leaders who are very effective at one place and time may become unsuccessful either when transplanted to another situation or when the factors around them change.
权变理论领导力模型主要是根据不同的情况和不同的环境来决定用什么样的领导方式,相信没有单一且特定的领导方式,这就是权变理论的核心。
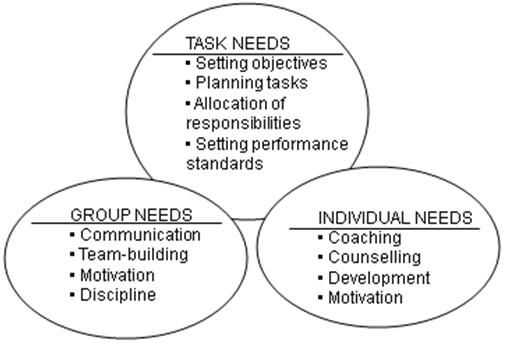
1. Action-Centred Leadership Model(行动力中心理论领导力模型)
John Adair's action-centred leadership model is where task, group and individual needs are interconnected. The total situation dictates the relative priority which must be given to each of the three sets of needs. Effective leadership means identifying and acting on that priority to create a balance between the needs.
2. Fiedler's Contingency Theory of Leadership(Fiedler权变理论领导力模型)
Fiedler found that people become leaders partly because of their own attributes and partly because of the nature of the situation they find themselves in. Leadership style depends on the personality of the leader, which is fixed. The extent to which the situation favours the leader depends on three things:
Fiedler found that a task-oriented was most productive when the situation was either very favourable to the leader or very unfavourable.
In less extreme cases, a more people-centred approach was more effective.
3. Handy's "Best Fit" Approach(Handy的Best-fit理论)
Charles Handy's best fit approach identifies four factors which a successful leader must integrate:
| 1. The leader personality, character and style |
| 2. Subordinates individual and collective personalities and preference for style of leadership |
| 3. The task objectives, technology and methods of working |
| 4. The environment |
From the first three of these factors, Handy creates a spectrum ranging from "tight" to "flexible".
Handy's "best fit" occurs where all three factors are at the same point in the spectrum. Almost inevitably there will be a misfit, and change will be necessary. Any such change is invariably slow.
| Tight | Flexible | |
| Leader | • Preference for autocratic style • Arrogant and contemptuous of subordinates • Dislikes uncertainty |
•Preference for democratic style •Confident in subordinates •Dislikes stress •Accepts reasonable risk and uncertainty |
| Subordinates | • Low opinion of own abilities • Do not like uncertainty in their work and like to be ordered • Regard their work as trivial • Past experience in work leads to acceptance of orders • Cultural factors lean them towards autocratic/dictatorial leaders |
•High opinion of own abilities •Like challenging, important work •Prepared to accept uncertainty and longer timescales for results • Cultural factors favour independence |
| Task | • Job requires no initiative, routine and repetitive or has a certain outcome • Short timescale for completion • Trivial tasks |
•Important tasks with a longer timescale •Problem-solving or decision-making involved • Complex work |
Copyright © 2000 - 2025 www.chinaacc.com All Rights Reserved. 北京正保会计科技有限公司 版权所有
京B2-20200959 京ICP备20012371号-7 出版物经营许可证 ![]() 京公网安备 11010802044457号
京公网安备 11010802044457号